商家描述
产品评价(0)
Clone
122 (See other available formats)
Regulatory Status
RUO
Workshop
HCDM listed
Other Names
TR2, Herpesvirus entry mediator A, Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 14, TNFRSF14, Tumor necrosis factor receptor like 2, HVEM
Isotype
Mouse IgG1, κ
Antigen Details
Structure
Member of the TNFR superfamily, type I transmembrane protein containing 2 TNF receptor domains. Predicted molecular weight approximately 30 kD.
Distribution
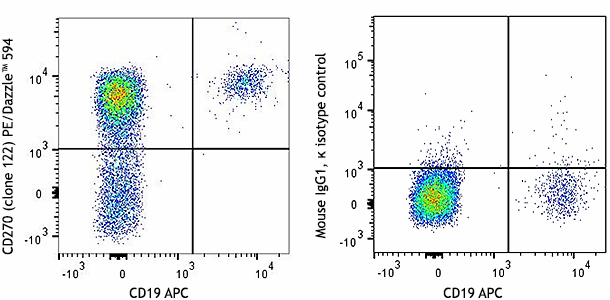
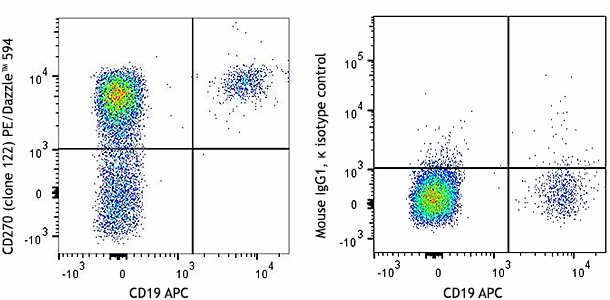
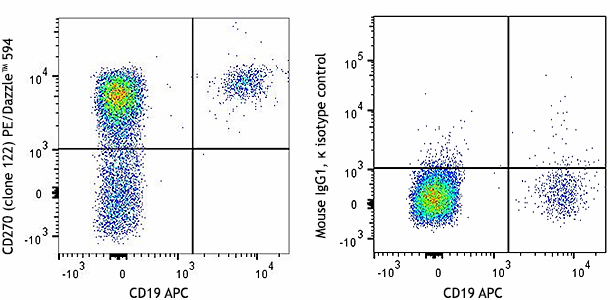
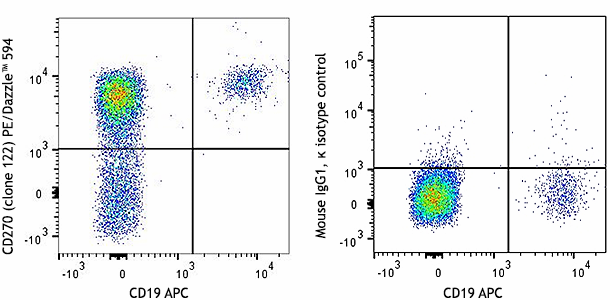
Widely expressed in blood vessels, brain, heart, kidney, liver, lung, prostate, spleen, thymus and other organs. Resting T cells and naïve and memory B cells express high levels of HVEM. Immature dendritic cells express high levels of HVEM that is downregulated upon maturation.
Function
Plays an important role in herpes simplex virus pathogenesis by enhancing entry into cells. Signaling through HVEM activates JNK1, NF-κB and AP-1 to control gene expression in response to infection or cellular stress and activate the immune response.
Interaction
TRAF1, TRAF2, TRAF3, TRAF5, B and T lymphocyte associated protein (BTLA), and estrogen receptor alpha have been shown to directly interact with HVEM in vivo.
Ligand/Receptor
LIGHT (TNFSF14), LTα
Cell Type
B cells, Dendritic cells, T cells
Biology Area
Cell Adhesion, Cell Biology, Immunology, Signal Transduction
Molecular Family
Adhesion Molecules, CD Molecules
Antigen References
1. Carfi A, et al. 2001. Molec. Cell 8:169.
2. Gonzalez LC, et al. 2005.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 102:1116.
3. Kwon BS, et al. 1997. J. Biol. Chem. 272:13471.
4. Marsters SA, et al. 1997. J. Biol. Chem. 272:14272.
5. Montgomery RI, et al. 1996. Cell 87:427.
Gene ID
8764
The 122 antibody recognizes human HVEM also known as herpesvirus entry mediator A, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 14, TNFRSF14, and tumor necrosis factor receptor like 2. HVEM, a member of the TNFR superfamily, is a type I transmembrane protein containing 2 TNF receptor domains with a predicted molecular weight of approximately 30 kD. HVEM is widely expressed in blood vessels, brain, heart, kidney, liver, lung, prostate, spleen, thymus and other organs. Resting T cells and naïve and memory B cells express high levels of HVEM as well. In humans, HVEM is not expressed in germinal center B cells. Immature dendritic cells express high levels of HVEM that is downregulated upon maturation. HVEM plays an important role in herpes simplex virus pathogenesis by enhancing entry into cells. Signaling through HVEM activates JNK1, NF-κB and AP-1 to control gene expression in response to infection or cellular stress and activate the immune response. HVEM binds to LIGHT and has also been shown to associate with several other proteins including TRAF1, TRAF2, TRAF3, TRAF5, B and T lymphocyte associated protein (BTLA), and estrogen receptor alpha.














 会员登录
会员登录.getTime()%>)
 购物车()
购物车()


 成功收藏产品
成功收藏产品